Rhabdomyolysis for the Correctional Nurse
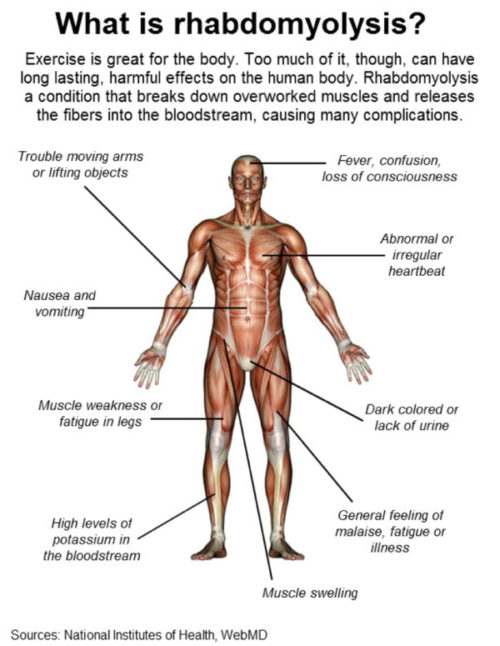
Rhabdomyolysis means the “dissolution of skeletal muscle”. It is a syndrome caused by direct muscle injury, or a mismatch between energy production and energy consumption that results in a breakdown of muscle cells. This breakdown results in the leakage of potentially toxic intracellular contents into the systemic circulation. While there are many causes for rhabdomyolysis, the most common include trauma, drugs, and strenuous exercise. The classic symptoms of rhabdomyolysis include a triad of muscle weakness, myalgia, and dark urine. It was initially described in the victims of crush injury during World War II, and was called the Meyer Betz disease. Management of rhabdomyolysis consists primarily of the correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities. Nursing interventions include conducting a thorough history and physical, obtaining ordered lab tests, hydration, patient monitoring and patient education.